Grant Deed Essentials for Commercial Real Estate Investors

Key Takeaways
- Grant deeds provide limited warranties covering only the grantor's period of ownership, not historical title issues.
- Commercial investors use grant deeds to balance protection and transaction feasibility.
- Grant deeds enable faster closings than warranty deeds while offering more security than quitclaim deeds.
- Title insurance supplements grant deed protections by covering pre-existing defects not warranted by the deed.
What is a Grant Deed?
A grant deed is a legal document that transfers property ownership. It moves title from the grantor to the grantee while providing limited warranties.
The grant deed assures that the grantor has not previously sold or place any liens or claims the property. Its main role is to record clear ownership of the property.
This document is key in property transactions, similar to how a land trust can be used in certain transfers.
Grant Deed Fundamentals for Commercial Real Estate
The grant deed sets out the terms of the property transfer. It offers basic assurances, which provide more security than a quitclaim deed but less than a general warranty deed.
This form of deed is used to record clear title and support sound commercial real estate investment strategies.
Commercial Implications
In commercial settings, grant deeds affect multi-tenant buildings, development parcels, and income producing assets. They help investors understand the title status before closing a deal.
For instance, when buying commercial property, it is important to know the deed's limits in protecting against past title issues.
Portfolio Strategy Considerations
Investors may use grant deeds when they have confidence in the property history. This deed type fits various investment plans and exit strategies in different types of commercial real estate.
Understanding the deed's structure helps in managing risk and planning for long term growth.
Why Commercial Investors Choose Grant Deeds
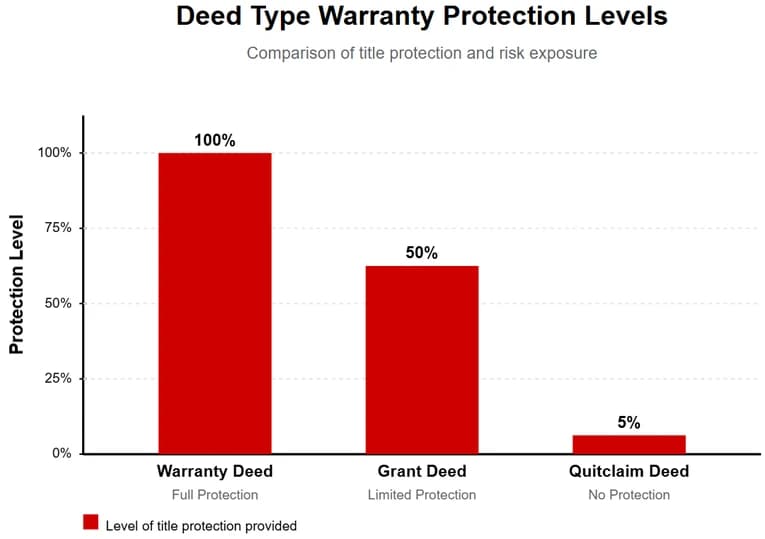
Grant deeds strike a strategic balance for commercial real estate transactions, offering more protection than quitclaim deeds while avoiding the extensive liability exposure that warranty deeds place on sellers.
Commercial investors favor grant deeds when acquiring properties with documented ownership history during the seller's tenure but unknown prior title conditions. The limited warranty covers the seller's period of ownership without extending liability to historical issues, making transactions more feasible for sellers while still providing meaningful protection to buyers.
This middle ground approach proves especially valuable in commercial portfolio acquisitions, development deals, and institutional transactions where comprehensive title insurance supplements the deed's limited warranties. Grant deeds enable faster closings than warranty deeds while offering significantly more security than quitclaim transfers.
Key Considerations for Deed Selection
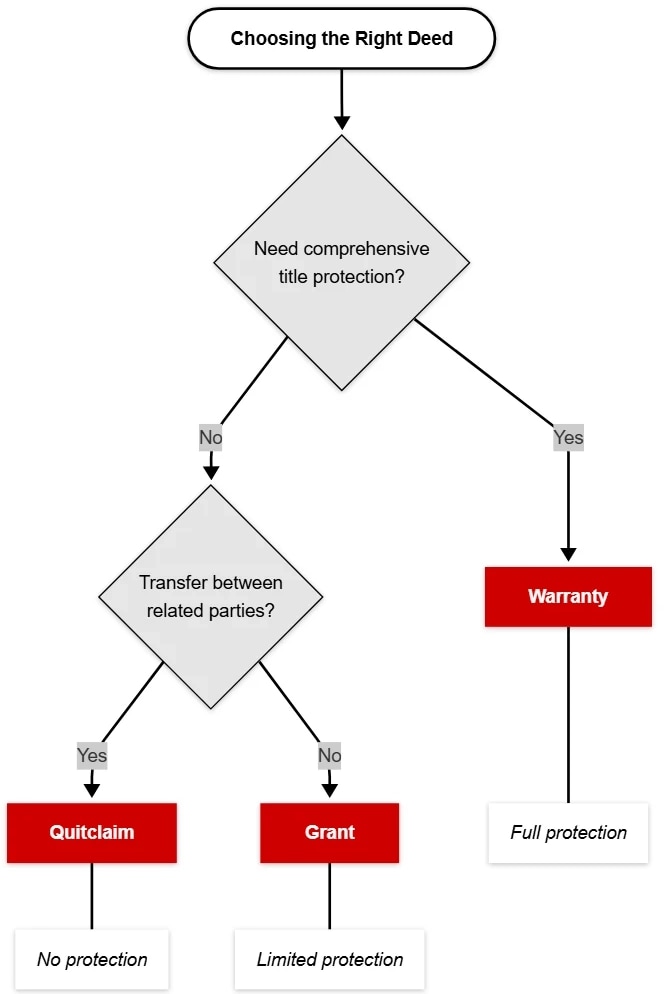
When selecting a deed type, commercial investors should weigh several key factors:
- Property Class: For high risk properties like multi-tenant buildings, a warranty deed may offer the comprehensive protection needed. Properties with clear title histories might be suited to a grant deed.
- Transaction Timeline: Quick transactions can benefit from the simplicity of a grant deed, while longer term deals may justify the added security of a warranty deed.
- Risk Tolerance: Investors with a low tolerance for risk should consider deeds with full title guarantees. Those comfortable with moderate risk might opt for a grant deed if the title is well-documented.
This structured approach ensures that the selected deed aligns with both the legal requirements and the financial strategy of the investment.
Sector Specific Considerations
Different commercial sectors handle deed selection in varied ways. Retail, industrial, office, and hospitality properties each face unique risks. This leads to different choices based on the property's use and investor goals.
Legal Requirements & Essential Components
A valid grant deed must include specific elements to be legally binding. It outlines the property description, identifies the parties, and states the granting clause clearly.
Essential Elements
The deed must have a clear legal description of the property. It should list the names and addresses of the grantor and grantee, the date, and the consideration given.
Notarized signatures and a proper granting clause are essential to confirm the transfer.
| Essential Element | Description | Importance / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Description | Detailed description of the property, including boundaries and location | Critical for ensuring the correct property is transferred |
| Party Details | Names and addresses of the grantor and grantee | Ensures accurate identification of involved parties |
| Granting Clause | Statement of intent to transfer property | Clearly states the purpose of the deed |
| Consideration | Details the payment or compensation for the transfer | Confirms that the transfer is a bona fide transaction |
| Notarized Signatures | Signatures of both parties must be notarized | Prevents fraud and ensures authenticity |
State by State Variations
Requirements can change by state, especially for commercial properties. Investors must check local regulations to ensure compliance.
This is important when dealing with a reciprocal easement agreement or when assessing variance in real estate guidelines, which can affect the allowable uses of a property and its market value.
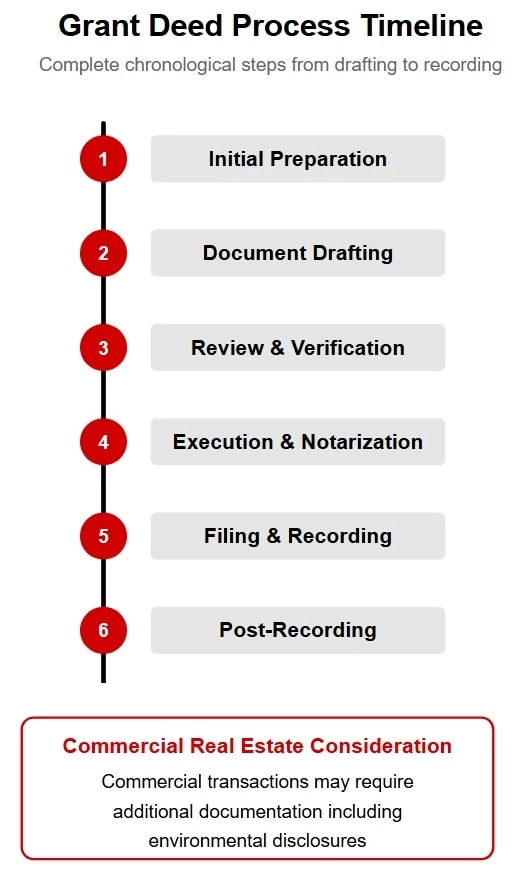
Commercial Provisions & Disclosures
Commercial transactions may require additional disclosures such as environmental conditions and zoning restrictions. These details protect both buyer and seller.
Understanding land zoning is crucial because zoning rules determine how land can be used and impact property value, which in turn affects the assurances a grant deed can offer.
Recording Process
Recording the grant deed makes the property transfer official. It creates a public record that helps secure ownership rights.
Filing and Public Record
After notarization, the deed must be filed with the county recorder's office. This filing protects your investment and is a critical step in real estate transactions.
For example, when you sell commercial property, having a properly recorded deed is crucial for clear title transfer.
Additional Legal Safeguards
Filing the deed on time ensures that any challenges to the title are managed promptly. This process can also work in tandem with a lien waiver to further secure the transaction.
Commercial Real Estate Specific Applications
Grant deeds play a key role in commercial financing and property management. They affect how investors secure and manage assets.
Financing and Lender Requirements
Grant deeds interact with financing by meeting lender requirements. Lenders often review deeds as part of CRE loans documentation.
This ensures that the property title is clear before funds are released.
Portfolio Management and Development Strategies
When building a commercial portfolio, keeping track of title records is crucial. A recorded grant deed helps maintain title integrity across multiple properties.
For investors planning a 1031 exchange, clear title documents streamline the process and protect investment value.
Exit Strategy and Transaction Efficiency
Grant deeds also impact exit strategies. They define the limits of title warranties and influence buyer perceptions during a sale. The limited warranty offered by a grant deed simplifies due diligence, enabling buyers to assess risks more quickly. This clarity in title protection can expedite the sales process and enhance overall transaction efficiency.
Additionally, some investors may explore alternative financing methods, such as owner financing, to create smoother exit pathways. This approach connects to exit strategies by offering flexible financing options that appeal to buyers when the grant deed's risk profile is acceptable to both parties.
Explore current commercial property listings in your area to see real world examples of assets that might involve grant deed transfers.
Commercial Real Estate For Sale
Strategic Considerations in Commercial Transactions
Investors must assess title risks and structure their entities wisely when dealing with grant deeds. Strategic planning reduces risk and improves transaction efficiency.
Pre-Acquisition Analysis
Before buying a property, perform a thorough title review to check for any liens, encumbrances, or chain of title issues. Also consider using a property valuation calculator to estimate the property's potential value based on monthly rental income, expenses, and cap rate. This combined approach helps you identify both legal and financial red flags before committing to a purchase.
Entity Structuring Strategies
Choosing the right business structure protects your personal assets in commercial transactions. Proper entity structuring can limit liability when acquiring properties with grant deeds.
For some investors, a tenancy in common arrangement offers a way to share ownership while keeping individual interests separate. Consider how a triple net lease arrangement might impact your risk and return expectations.
Investor Checklist & Due Diligence Guide
Investors must complete a thorough checklist before acquiring properties with a grant deed. This guide helps identify title risks and safeguards your investment.
Pre-Acquisition Checklist
- Review all title documents and verify the grant deed is correctly recorded.
- Confirm there are no unresolved liens, encumbrances, or title disputes.
- Ensure the legal description of the property is accurate and complete.
- Check that all required signatures and notarizations are in place.
- Assess any potential transfer taxes or local recording fees.
Professional Team Assembly
Build a team of experts including real estate attorneys, title officers, and inspectors. Their expertise can prevent costly errors in the transfer process.
Consider hiring a realtor for commercial property to help manage the process.
Red Flag Identification
Establish a system to spot potential issues like unresolved liens or errors in the legal description. Early identification can reduce risk and prevent financial loss.
A thorough commercial appraisal provides valuable insight into the property's condition and value.
Frequently Asked Questions
What unique challenges do multi-tenant commercial properties present when transferred via grant deed?
Multi-tenant properties require careful review of tenant agreements and lease compliance. You must verify tenant estoppel certificates and confirm that all leasehold improvements have the proper permits. Additionally, review common area maintenance (CAM) charges and check for any ongoing tenant disputes that might carry over after the transfer.
How are blockchain and AI technologies changing the due diligence process for commercial properties acquired through grant deeds?
Blockchain creates an unalterable record of property ownership, reducing the risk of fraudulent transfers. AI tools quickly scan historical records to identify title defects and potential issues that might not be covered by a grant deed. These technologies streamline the due diligence process, ensuring all grant deed requirements are met more efficiently.
When negotiating commercial property acquisitions, how can I request a warranty deed instead of a grant deed without derailing the deal?
Begin by obtaining a preliminary title report to highlight specific risks. Present your request as a fair risk allocation measure rather than a personal critique of the seller. You might suggest a warranty deed with a time limit or a title indemnity agreement, which can enhance protection without jeopardizing the overall deal.
